This data sheet provides an overview of features, benefits, and product availability of the Cisco® Router and Security Device Manager (SDM).
Cisco SDM is an intuitive, Web-based device-management tool for Cisco IOS® Software-based routers. The Cisco SDM simplifies router and security configuration through smart wizards, which help customers and Cisco partners quickly and easily deploy, configure, and monitor a Cisco router without requiring knowledge of the command-line interface (CLI). The Cisco SDM is supported on a wide range of Cisco routers and Cisco IOS Software releases. Refer to Table 3 for specific model numbers supported by the Cisco SDM.
Ease of Use and Built-In Application Intelligence
The Cisco SDM allows users to easily configure routing, switching, security, and quality-of-service (QoS) services on Cisco routers while enabling proactive management through performance monitoring (see Figure 1). Cisco SDM users can remotely configure and monitor their Cisco routers without using the Cisco IOS Software CLI. The Cisco SDM GUI aids non-expert users of Cisco IOS Software in their day-to-day operations, provides easy-to-use smart wizards, automates router security management, and assists users through comprehensive online help and tutorials.
Figure 1. Cisco SDM Homepage
Cisco SDM smart wizards guide users step by step through router and security configuration workflow by systematically configuring LAN, WLAN, and WAN interfaces; firewalls; intrusion prevention systems (IPS); and IP Security (IPsec) VPNs. Cisco SDM smart wizards can intelligently detect incorrect configurations and propose fixes, such as allowing Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) traffic through a firewall if the WAN interface is DHCP-addressed. Online help embedded within the Cisco SDM contains appropriate background information, in addition to step-by-step procedures to help users enter correct data in the Cisco SDM. Networking and security terms and definitions that users might encounter are included in an online glossary.
For network professionals familiar with Cisco IOS Software and its security features, the Cisco SDM offers advanced configuration tools to quickly configure and fine-tune router security features, allowing network professionals to review the commands generated by the Cisco SDM before delivering the configuration changes to the router.
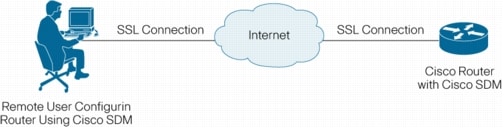
The Cisco SDM helps administrators configure and monitor routers in remote locations using Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Secure Shell (SSHv2) Protocol connections (see Figure 2). This technology enables a secure connection over the Internet between SDM on the user's laptop and the router. When deployed at a branch office, a Cisco SDM-enabled router can be configured and monitored from corporate headquarters, reducing the need for experienced network administrators at the branch office.
Figure 2. Connecting to a Cisco SDM-Enabled Router Using SSL for Secure Remote Connectivity
Integrated Security Configuration
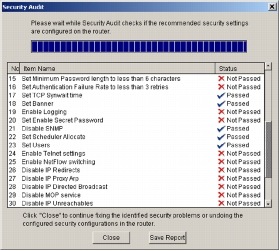
When deploying a new router, Cisco SDM users can configure a Cisco IOS Software firewall quickly and using the best practices recommended by the International Computer Security Association (ICSA) and the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC). An advanced firewall wizard allows a single-step deployment of high, medium, or low application firewall policy settings. Cisco SDM users can configure the strongest VPN defaults and automatically perform security audits (see Figure 3). In addition, Cisco SDM users can perform one-step router lockdown for firewalls and one-step VPN for quick deployment of secure site-to-site connections. A recommended list of IPS signatures bundled with Cisco SDM allows quick deployment of worm, virus, and protocol exploit mitigation. The Cisco SDM Network Admission Control (NAC) wizard enables simple and fast integration of NAC and client security posture management into an existing network infrastructure.
Figure 3. Router Security Audit
When invoked on an already configured router, Cisco SDM allows users to perform one-step security audits to evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of their router configurations against common security vulnerabilities. Administrators can fine-tune their existing router security configurations to better suit their business needs. The Cisco SDM also can be used for day-to-day operations such as monitoring, fault management, and troubleshooting.
Router Configuration
In addition to security configuration, Cisco SDM helps users quickly and easily configure router services such as LAN, WLAN, and WAN interface configuration; dynamic routing; DHCP server; QoS policy; and so on.
Using the LAN configuration wizard, users can assign IP addresses and subnet masks to Ethernet interfaces and can enable or disable the DHCP server. Using the WAN configuration wizard, users can configure xDSL, T1/E1, Ethernet, and ISDN interfaces for WAN and Internet access. Additionally, for serial connections, users can implement Frame Relay, Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), and High-Level Data Link Control (HDLC) encapsulation. Cisco SDM also allows configuration of static routing and common dynamic routing protocols such as Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), Routing Information Protocol (RIP) Version 2, and Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP).
QoS policies can easily be applied to any WAN or VPN tunnel interface using Cisco SDM. The QoS policy wizard automates the Cisco architecture guidelines for QoS policies to effectively prioritize the traffic between real-time applications (voice or video), business-critical applications (Structured Query Language [SQL], Oracle, Citrix, routing protocols, and so on), and the rest of network traffic (for instance, Web and e-mail traffic). Monitoring based on network based application recognition (NBAR) in the Cisco SDM allows users to visually inspect the application layer traffic in real time and confirms the effect of QoS policies on different classes of application traffic.
Monitoring and Troubleshooting
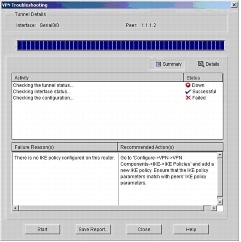
In monitor mode, Cisco SDM provides a quick, graphical status of important router resources and performance measurements such as the interface status (up or down), CPU, and memory usage (see Figure 4). For wireless models, Cisco SDM provides comprehensive support for real-time 802.11 a/b/g interface statistics. Cisco SDM takes advantage of integrated routing and security features on routers to provide in-depth diagnostics and troubleshooting of WAN and VPN connections. For example, while troubleshooting a failed VPN connection, the Cisco SDM verifies the router configurations and connectivity from the WAN interface layer to the IPsec Crypto Map layer. While testing configuration and remote-peer connectivity at each layer, Cisco SDM provides pass or fail status, possible reasons of failure, and Cisco TAC-recommended actions for recovery.
Figure 4. VPN Troubleshooting and Recovery
Cisco SDM monitor mode also allows users to view the number of network access attempts that were denied by the Cisco IOS Software firewall and it provides easy access to the firewall log. Users also can monitor detailed VPN status, such as the number of packets encrypted or decrypted by IPsec tunnels, and Easy VPN client session details.
Table 1 describes the features that are new in Cisco SDM Version 2.5.
Table 1. Cisco SDM Features New in Version 2.5
| Feature | Benefit |
| Cisco Easy VPN Features |
| • Configures password expiry using AAA • Configures split DNS • Configures Cisco Tunneling Control Protocol • Configures per-user AAA policy download with PKI • Configures identical addressing | Allows provisioning of a rich set of Easy VPN security features across Cisco IOS software releases in 12.4 T train. |
| Cisco SSL VPN Features |
| • Configures port forwarding • Configures radius accounting • Configures application ACL support • Configures URL Obfuscation • Transcend Client Support Phase 1 | Allows provisioning of a rich set of SSL VPN security features across Cisco IOS software releases in 12.4 T train. |
| WAAS NM Support |
| • NME-WAE-502-K9 • NME-WAE-522-K9 • NME-WAE-302-K9 • Configures WCCP on the router and IP address on the WAE module. Registers the IP address of the WAE module with the central WAAS manager. | Single user interface for the initial provisioning and ongoing monitoring of the network module. |
| Airlink Phase II Support |
| Advanced Encryption Service (AES), IEEE 802.1x Local authentication service for EAP-FAST, SSID globalization, Multiple Basic Service Set ID (BSSID), wireless root, nonroot bridge and universal client mode, multiple encrypted VLANs, VLAN assignment by name, Wi-Fi multimedia required elements | Allows configuration of a rich set of wireless features on the router. |
| Cable Hardware Supported |
| • Cisco c815 router • HWIC-CABLE-D-2 • HWIC-CABLE-E/J-2 | Configures IP address on the WAN interface and monitoring of key statistics like bandwidth on upstream and downstream traffic |
| Additional 18xx hardware supported | CISCO1801-M/K9, CISCO1801W-AG-E/K9, CISCO1801W-AG-C/K9, CISCO1801WM-AGE/K9, CISCO1801W-AG-A/K9, CISCO1801W-AG-N/K9, CISCO1802W-AG-E/K9, CISCO1803W-AG-A/K9, CISCO1803W-AG-E/K9, CISCO1811W-AG-A/K9, CISCO1811W-AG-C/K9, CISCO1811W-AG-N/K9, CISCO1812/K9, CISCO1812-J/K9, CISCO1812W-AG-P/K9, CISCO1812W-AG-C/K9, CISCO1812W-AG-E/K9, CISCO1812W-AG-J/K9, CISCO 1801, CISCO1801/K9, CISCO1801W-AG-B/K9, CISCO1802, CISCO1802/K9, CISCO1802, CISCO1903/K9, CISCO1803G-B/K9, CISCO1811/K9, CISCO1811W-AG-B/K9 |
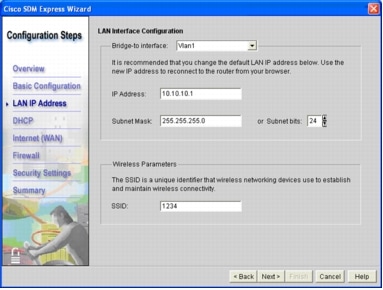
Figure 5. Cisco SDM Express
Cisco Router Mass Deployments
Cisco SDM is integrated with the Cisco CNS 2100 Series Intelligence Engine to help enable fast and cost-effective mass deployments of Cisco routers with factory default configurations. Service providers and large enterprises have the flexibility to use the Cisco SDM and Cisco CNS 2100 Series combination during staging or allow an untrained, onsite administrator to download the final Cisco IOS Software configuration without using the Cisco IOS Software CLI.
Cisco Router Security Management
Cisco SDM helps Cisco partners and customers easily deploy Cisco IOS Software security features-Network Address Translation (NAT), access control lists (ACLs), firewalls, intrusion prevention system (IPS), and IPsec VPNs-and integrates these security features into existing router configuration and network architectures. Smart wizards in the Cisco SDM understand the interaction of routing and security features and guide the user to a final configuration that is approved and tested by the Cisco TAC from end to end. The CLI preview mode in the Cisco SDM allows expert users to manually validate the final configuration before it is delivered to the router.
Cisco Router Operational Management
Cisco SDM helps Cisco partners and customers securely (using SSL and SSH) and remotely manage all critical aspects of router operations: hardware and software inventory status, interface status, firewall and ACL logs, VPN tunnel status, and most recent syslog messages. Figure 6 shows Cisco SDM hardware and software inventory details.
Figure 6. Cisco Router Hardware and Software Inventory
Conclusion
The Cisco SDM is a valuable productivity-enhancing tool for network and security administrators. Cisco partners can use the Cisco SDM for faster and easier deployment of Cisco routers for both WAN access and network security features.
Cisco customers can use the Cisco SDM for reducing the total cost of ownership of their Cisco routers by relying on Cisco SDM-generated configurations that are tested end to end by Cisco engineers and approved by the Cisco TAC. Configuration checks built into Cisco SDM reduce the instances of configuration errors.
Product Specifications
Table 2 shows primary features and benefits of the Cisco SDM. Table 3 shows product specifications for the Cisco SDM.
Table 2. Cisco SDM Primary Features and Benefits
| Feature | Benefit |
| Embedded Web-based Management Tool | • Turns the router into a complete security and remote-access solution with its own management tool • Does not require a dedicated management station • Allows remote management from any supported desktop or laptop |
| SSL- and SSHv2-based Secure Remote Access | • Provides for secure management across the WAN |
| At-a-Glance Router Status Views | • Offers quick graphical summary of router hardware, software, and primary router services such as VPN, firewall, QoS, etc. |
| Router Security Audit | • Assesses vulnerability of existing router • Provides quick compliance to best-practices (Cisco TAC, ICSA recommendations) security policies for routers |
| One-Step Router Lockdown | • Simplifies firewall and Cisco IOS Software configuration without requiring expertise about security or Cisco IOS Software |
| Smart Wizards for Most Frequent Router and Security Configuration Tasks | • Generates Cisco TAC-approved configurations • Averts misconfigurations with integrated routing and security knowledge • Reduces network administrators' training needs for new Cisco IOS Software security features • Secures the existing network infrastructure easily and cost-effectively |
| Policy-Based Firewall and ACL Management (Firewall Policy) | • Allows security administrators to easily and quickly manage ACLs and packet-inspection rules through a graphical and intuitive policy table |
| IPS | • Allows easy and quick provisioning of Cisco tuned and recommended high-fidelity attack signatures on any router interface for inbound and outbound traffic • Allows dynamic update of new IPS signatures without impacting basic router operations • Allows graphical customization of IPS signatures for immediate response to new worm or virus variants • Allows filtering of signatures and mass configuration changes (action or severity) for the selected signatures • Shows real-time status and error messages from IPS engine |
| Cisco Easy VPN Server | • Offers wizard-based configuration and real-time monitoring of remote-access VPN users • Provides integration with on-router or remote authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) server |
| Role-Based Access | • Offers logical separation of router between different router administrators and users • Provides for secure access to Cisco SDM user interface and Telnet interface specific to each administrator's profile • Helps enable Cisco value-added resellers and service providers to offer a graphical, read-only view of the CPE services to end customers • Offers factory-default profiles: • Administrator • Firewall administrator • Easy VPN client user • Read-only user |
| WAN and VPN Troubleshooting | • Reduces mean time to repair (MTTR) by taking advantage of the integration of routing, LAN, WAN, and security features on the router for detailed troubleshooting • Takes advantage of integration of routing, LAN, WAN, and security features on the router for detailed troubleshooting of IPsec VPNs or WAN links • Integrates Layer 2 and above troubleshooting with Cisco TAC knowledge base of recovery actions |
| QoS Policy | • Easily and effectively optimizes WAN and VPN bandwidth and application performance for different business needs (voice and video, enterprise applications, Web, etc.) • Three predefined categories: real time, business critical, and best effort |
| NBAR | • Provides real-time validation of application usage of WAN and VPN bandwidth against predefined service policies • Provides for traffic performance monitoring |
| SSHv2 | • Provides for secure management between PC and Cisco router • Automatically uses SSHv2 for all encrypted communication between Cisco SDM and router |
| Real-Time Monitoring and Logging | • Allows administrators to proactively manage router resources and security before they affect mission-critical applications on the network |
| Digital Certificates | • Offers highly scalable and more secure solution than preshared keys • Now easy to use and deploy with the combination of Cisco SDM, Cisco IOS Certificate Authority Server, and Easy Secure Device Deployment (EzSDD) feature. |
| Real-Time Network and Router Resource Monitoring | • Offers faster and easier analysis of router resource and network resource usage • Offers graphical charts for LAN and WAN traffic and bandwidth usage |
| Task-Based Cisco SDM User Interface | • Provides for faster and easier configuration of security configurations-IPsec VPNs, firewall, ACLs, IPS, etc. • Offers quick snapshot of router services configuration through dashboard view on the homepage |
| Cisco SDM Express Wizard-Based Deployment of Router | • Offers quick and easy router deployment for basic WAN access configurations • Ideal router deployment tool for nonexpert users |
| PC-Based SDM Cisco SDM Installed on Windows-based PC Instead of Router Flash Memory | • No extra Flash memory space required on router for Cisco SDM • Great tool to manage the installed base of Cisco routers |
| Localized in Six Languages | • Simplifies router management for users in six different languages • Cisco SDM user interface and online help translated in Japanese, Simplified Chinese, French, German, Spanish, and Italian • Microsoft Windows OS support for these languages (available now) |
| Integrated Wireless Management | • Express Setup wizard simplifies the first-time setup of wireless interface • Advanced Web-based configuration and monitoring available • Reduces time and skill set required to bring up wireless interfaces • Flexibility to customize wireless configuration and security based on site-specific needs |
| IPS Provisioning Improvement | • Allows rapid deployment of IPS signatures specific to router model |
| Cisco Incident Control Services (ICS) |
| • Support Trend Micro signatures | • Allows rapid deployment and customization of signatures for day-zero protection against new attacks |
| Network Admission Control (NAC) |
| • Configuration wizard and client security posture management on routers | • Provides simple and fast integration of NAC into existing network infrastructure |
| Application Firewall |
| • Advanced firewall wizards, policy views, inspection rule editors, and log views • Peer-to-peer (P2P) applications: BitTorrent, Kazaa, Gnutella, eDonkey • Instant Messaging: Yahoo, MSN, AOL • Protocol conformance: HTTP and e-mail (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol [SMTP], ESMTP, POP3, and Internet Message Access Protocol [IMAP]) | • Delivers application-level control and unified threat management for accelerated security solutions deployment • Provides protocol anomaly detection services • Provides high, medium, and low security levels for firewall policy settings to enable accelerated and easy deployment • Low-For business environments that do not need to track P2P and IM applications on the network or check for protocol conformance • Medium-For business environments where security is important and there is a need to track the use of IM and P2P applications and check for HTTP and e-mail protocol conformance • High-For business environments where security is critical, and there is a need for protocol anomaly detection services to drop non conformant HTTP and e-mail traffic and prevent use of P2P and IM applications |
| Granular Protocol Inspection |
| • User-customizable application to port (or port range) mapping over TCP and UDP ports | • Provides menu of applications for easy and granular protocol selection in policies |
| Threat-Based Intrusion Protection |
| • Threat-based signature categories to ease IPS deployments • IPS configuration wizards, event viewer | • Provides easier and more intelligent signature selection based on available resources and attack categories (such as viruses, worms, Trojans, denial-of-service, and distributed-denial-of-service attacks) • Provides real-time reporting of signature engine status |
| Easy VPN Server and Remote Enhancements |
| • Advanced wizards, remote configuration update, Web intercept, dial backup, and QoS support | • Scalable, easy-to-manage, secure remote access for teleworkers or small offices on hub routers or branch office access routers |
| Dynamic DNS |
| • HTTP-based and IETF-based updates • Integration with existing WAN interface configuration wizard | • Enables scalable, remote management of dynamically addressed routers • Makes it possible to run business services without dedicated and expensive static IP addresses |
| Integrated Cisco IOS WebVPN Management |
| • Wizard-based configuration and real-time monitoring of WebVPN features • Persistent self-signed certificates | • Enables rapid and easy to manage deployment of secure remote access connectivity for teleworkers and small office branch routers |
| • IPS Security Dashboard • Integration with Cisco IPS alert center • IPS Signature import UI | • Enables real-time updates on top threats from MySDN site • Enables easier and more intelligent IPS signature selection and updates based on top threats |
| • Network- and application-level monitoring • Netflow-based Top N statistics, application traffic monitoring, search operations on event tables | • Provides easy-to-comprehend performance monitoring for day-to-day operations and troubleshooting • Enables better visibility into network and application performance • Makes it easy to identify unusual traffic patterns and application usage |
| • URL filtering • Configure and manage Black and White list of URLs | • Enables rapid deployment and customization of on-box URL filtering • Provides an easy and cost-effective solution to control Web access for employees based on corporate policies |
| • Launch point for high-volume deployments • Integration with Secure Device Provisioning (SDP), CNS and eToken device provisioning | • Enables zero-touch provisioning for rapid deployment of managed CPE devices and services |
| • Cisco IOS router image management • Easy to use UI for router image upgrades • Validation and conformance of IOS image with router hardware | • Reduces cost of operations and improves router uptime for IOS image upgrade and maintenance |
| • VPN design wizard | • Quick and easy selection of VPN technology based on deployment model |
Table 3. Product Specifications for Cisco SDM (Minimum Cisco IOS Software Releases Supported)
| Feature | Detailed Specification |
| Supported Platforms | • Cisco Small-Business 101 Router, Cisco Small-Business 106 Router, Cisco Small-Business 107 Router: • Cisco IOS Software Release 12.3(8)YG • Cisco 831 Ethernet Broadband Router, Cisco 836 ADSL over ISDN Broadband Router, and Cisco 837 ADSL Broadband Router: • Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(13)ZH or 12.3(2)T • Cisco 851, 856, 871, 876, 877, and 878 Integrated Services Routers: • Cisco IOS Software Release 12.3(8)YI • Cisco c815 router • Cisco IOS Software Release 12.4(6)XE • Cisco 1701 ADSL Security Access Router; Cisco 1710, 1711, and 1712 Security Access Routers; and Cisco 1721, 1751, 1751-V, 1760, and 1760-V Modular Access Routers: • Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(13)ZH, 12.2(13)T3, or 12.3(1)M • Cisco 1801, 1802, 1803, 1811, and 1812 Integrated Services Routers: • Cisco IOS Software Release 12.3(8)YI • Cisco 1841 Integrated Services Router: • Cisco IOS Software Release 12.3(8)T4 • Cisco 2610XM, 2611XM, 2620XM, 2621XM, 2650XM, and 2651XM and Cisco 2691 Multiservice Platforms: • Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(15)ZJ3, 12.2(11)T6, or 12.3(1)M • Cisco 2801, 2811, 2821, and 2851 Integrated Services Routers: • Cisco IOS Software Release 12.3(8)T4 • Cisco 3725 and 3745 Multiservice Access Routers: • Cisco IOS Software Release 12.2(15)ZJ3, 12.2(11)T6, or 12.3(1)M • Cisco 3825 and 3845 Integrated Services Routers: • Cisco IOS Software Release 12.3(11)T • Cisco 7204VXR, 7206VXR, and 7301 routers: • Cisco IOS Software Release 12.3(2)T or 12.3(3)M; no support for B, E, and S trains |
| Software Compatibility | • Compatible with all Cisco IOS Software feature sets for the previously listed Cisco SDM-supported releases of Cisco IOS Software |
| Connectivity | • HTTP and HTTPS; Telnet, SSH, and SSHv2 |
| Basic Router Configuration Parameters | • Users with different access profiles • Domain Name System (DNS) • DHCP server and client • SNMP • Telnet, SSH, SSHv2, and vty • Date and time, Network Time Protocol (NTP) • Syslog • Reset to factory defaults • Host name, domain name, and banner |
| Advanced Router Configuration Parameters | • Routing protocols: static, RIP Versions 1 and 2, OSPF, and EIGRP • NAT (static and dynamic) • ACLs • QoS policies, NBAR • VLANs on Cisco EtherSwitch® ports • IP proxy Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) redirects, ICMP unreachable, ICMP mask reply, and directed broadcasts • AAA local or remote configuration |
| Configurable Router Interfaces | • Ethernet (10, 10/100, and 10/100/1000 Mbps) • 802.11 a, 802.11 b/g • xDSL (asymmetric DSL [ADSL] and G.SHDSL) • T1/E1 (serial) • ISDN Basic Rate Interface (BRI) with multilevel precedence and preemption • Analog modem • Cable |
| Supported WAN Encapsulations | • Frame Relay • PPP • PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE) • PPP over ATM (PPPoA) • RFC 1483 routing • HDLC • ADSL autodetect |
| Configurable VPN Parameters | • Internet Key Exchange (IKE), digital certificates, Data Encryption Standard (DES), Triple DES (3DES), Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), and compression • IPsec site to site • Cisco Easy VPN Server (including DVTI support ) • Cisco Easy VPN Remote (including DVTI support ) • Generic-routing-encapsulation (GRE) tunnel • Dynamic Multipoint VPN (DMVPN; both hub and spoke), including dynamic spoke to spoke with redundant hubs |
| Supported Firewall Parameters | • Context-based access control (CBAC), Common Classification Policy Language (C3PL) zone-based firewall, DMZ, firewall log, firewall and ACL policy view, secure management access |
| Supported IPS Features | • IPS rules for inbound or outbound traffic inspection, signature fine-tuning, signature customization, and SDEE error message display • Encrypted signature format, risk rating, automated signature update, IDCONF signature provisioning, individual and category-based signature provisioning |
| CiscoView Compatibility | • Usable with Cisco SDM |
| Cisco CallManager Express Compatibility | • Usable with Cisco SDM |
| Performance | • Cisco SDM has negligible impact on router DRAM or CPU. |
System Requirements
Table 4 lists the system requirements for the Cisco SDM.
Table 4. System Requirements
| Feature | Description |
| Router Flash Memory | • Minimum of 6 MB of free Flash memory on the router for Cisco SDM files • Minimum of 2 MB of free Flash memory on the router for Cisco SDM Express. Wireless Management file requires additional 1.7 MB. Rest of the SDM files can be installed on PC hard disk. |
| PC Hardware | • Pentium III or later series processor |
| PC Operating System | • Windows XP Professional • Windows 2003 Server (Standard Edition) • Windows 2000 Professional • Windows NT 4.0 Workstation (Service Pack 4) • Windows ME • Japanese, Simplified Chinese, French, German, Spanish, and Italian language OS support • Windows XP Professional • Windows 2000 Professional |
| Browser Software | • Microsoft Internet Explorer 5.5 or later • Netscape Navigator 7.1 and 7.2 • Firefox 1.0.5 |
| Java Software | • Java Virtual Machine (JVM) built-in browsers required • Java plug-in (Java Runtime Environment Version 1.4.2_05 or later) |
Ordering Information
Table 5 lists ordering and factory shipping options for the Cisco SDM.
Table 5. Ordering and Factory Shipping Options for Cisco SDM
| Feature | Description |
| Cisco 831 Ethernet Broadband Router, Cisco 836 ADSL over ISDN Broadband Router, Cisco 837 ADSL Broadband Router, Cisco Small-Business 100 Series Router, Cisco 850 Series Router, and Cisco 870 Series Router | • Cisco SDM software ships by default from factory. • SDM Express is factory installed on router Flash memory, and a Cisco SDM CD is bundled with the router. |
| Cisco 1700 Series Modular Access Routers and Cisco 2600XM Series Cisco 1800 Series Integrated Router ( except for Cisco 1841 model with 64 MB or higher flash memory ) | • Cisco SDM software ships by default on security bundles (k9). • Cisco SDM software $0 configuration option (ROUTER-SDM or ROUTER-SDM-NOCF) is available on all SKUs. • Cisco SDM Express is factory installed on router Flash memory, and a Cisco SDM CD is bundled with the router. |
| Cisco 1841 (64 MB Flash memory or higher ), 2800, and 3800 Series Integrated Services Routers | • Cisco SDM software ships by default from factory. • Cisco SDM is factory installed on router Flash memory. |
| Cisco 2691 Multiservice Platform and Cisco 3700 Series Multiservice Access Routers | • Cisco SDM software ships by default on security bundles (k9). • Cisco SDM software $0 configuration option (part number ROUTER-SDM or ROUTER-SDM-NOCF) is available on all SKUs. • Cisco SDM is factory installed on router Flash memory. |
| Cisco 7204VXR, 7206VXR, and 7301 Routers | • Cisco SDM software ships by default on security bundles (k9). • Cisco SDM software $0 configuration option (part number ROUTER-SDM or ROUTER-SDM-NOCF) is available on all SKUs. • Cisco SDM is factory installed on router Flash memory. |
For customers who want to use the AutoInstall feature in Cisco IOS Software, two US$0 SKUs are offered: ROUTER-SDM-NOCF and ROUTER-SDM-CD-NOCF. If either of these SKUs is ordered with a Cisco router, manufacturing loads Cisco SDM files only on the router Flash memory, and the default startup configuration is not loaded in the router's NVRAM.
To place an order, visit the
Cisco Direct Order page.
To Download the Software
Visit the
Cisco Software Center to download the latest Cisco SDM software that can be installed on a router Flash memory or on a PC.
Service and Support
Cisco offers a wide range of services to accelerate customer success. These innovative services are delivered through a unique combination of people, processes, tools, and partners, resulting in high levels of customer satisfaction. Cisco services help you protect your network investment, optimize network operations, and prepare your network for new applications to extend network intelligence and the power of your business. For more information about Cisco services, refer to
Cisco Technical Support Services.
For More Information
For more information about the Cisco SDM, visit
http://www.cisco.com/go/sdm or contact your Cisco account representative.


























 If you want to keep your Microsoft Office documents away from unwelcomed eyes, a good idea is to password-protect them. But what if you lose the password? Don’t worry. Petri has come up with a neat little tool to recover a password protected Microsoft Office document. Office Password Recovery Utility lets you decrypt Microsoft Office Word, PowerPoint, Outlook and
If you want to keep your Microsoft Office documents away from unwelcomed eyes, a good idea is to password-protect them. But what if you lose the password? Don’t worry. Petri has come up with a neat little tool to recover a password protected Microsoft Office document. Office Password Recovery Utility lets you decrypt Microsoft Office Word, PowerPoint, Outlook and